2022年10月21日,国家香蕉产业技术体系品种改良岗位的论文“Elucidating the role of MaBAM9b in starch degradation”在国际著名植物学期刊《Plant Science》(SCI, IF=5.363)上发表。刘菊华研究员和苗红霞研究员为论文共同第一作者,该论文得到金志强研究员和谢江辉研究员指导。该项工作得到财政部和农业农村部-国家现代农业产业技术体系资助。
作者:刘菊华1,苗红霞1,王宇迪,张建斌,张静,郑云柯,王静毅,贾彩红,徐碧玉,李新国,谢江辉*,金志强*
题目:MaBAM9b作用于淀粉降解的分子机制
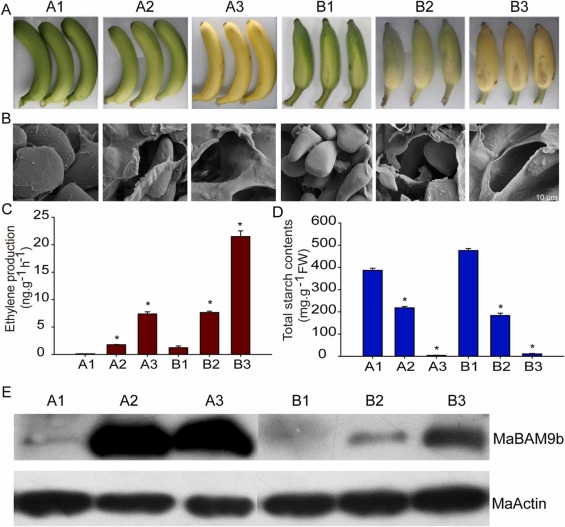
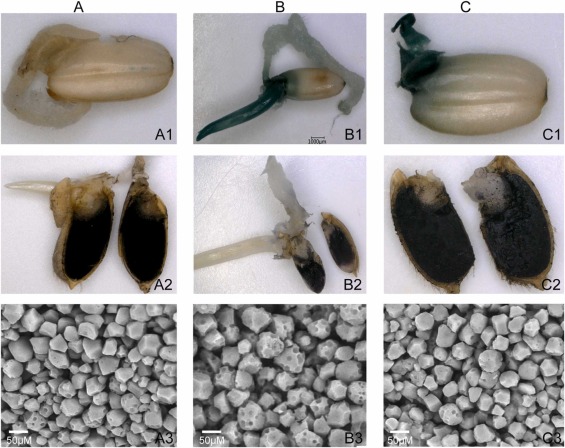
摘 要:香蕉是典型的淀粉转化型果实。采收时高淀粉,采后成熟过程中迅速降解并转化为可溶性糖,最终形成风味品质。这个过程受基因、环境因子等多种因素调节。MaBAM9b是前期通过转录组分析发现的在香蕉果实中高表达的基因,然而其在淀粉降解中的作用机制尚不清楚。本研究从香蕉果实中克隆到MaBAM9b全长,其亚细胞定位、蛋白表达模式和瞬时表达等特征被解析。此外,正义和反义MaBAM9b转化至水稻 (Oryza sativa L. japonica. cv. ‘Nipponbare’),以鉴定MaBAM9b功能。MaBAM9b全长为1599 bp,编码532个氨基酸,包括PLN02803和糖基水解酶家族14两个保守结构域,定位在叶绿体。MaBAM9b蛋白在香蕉果实成熟和淀粉降解过程中始终保持较高水平。香蕉果实薄片中瞬时过表达或沉默MaBAM9b表达,能够显著促进或抑制淀粉降解。水稻遗传学证据表明,MaBAM9b过表达促进了淀粉降解和显著提高了种子萌发,而抑制其表达显著阻碍了这些生物学过程。这些结果支持MaBAM9b在淀粉降解中的关键作用,并为香蕉果实品质改良和生物育种提供了一个关键靶基因。
全文链接:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2022.111497
Juhua Liu*,1, Hongxia Miao1, Yudi Wang1, Jianbin Zhang1, Jing Zhang, Yunke Zhen, Jingyi Wang, Caihong Jia, Biyu Xu, Xinguo Li**, Jianghui Xie**, Zhiqiang Jin**. Elucidating the role of MaBAM9b in starch degradation. Plant Science, 2022.
Abstract
Banana is a typical starch conversion fruit. The high content of starch at harvest is quickly digested and converted to soluble sugars during the postharvest ripening process, ultimately contributing to fruit flavor. This process is regulated in a complex manner by genes and environmental factors. MaBAM9b is one of the main enzyme genes previously found by transcriptomic analysis to be highly expressed in banana fruit. However, its exact role in starch degradation remains unclear. Here, full-length MaBAM9b was isolated from banana fruit, and its subcellular localization, protein expression, and transient expression in banana fruit slices were investigated. In addition, sense and anti-sense MaBAM9b were transformed into rice (Oryza sativa L. japonica. cv. ‘Nipponbare’) to identify the function of MaBAM9b. MaBAM9b was 1599 bp and encoded 532 amino acids. It contained two conserved domains of PLN02803 and glycosyl hydrolase family 14 was localized in the chloroplast. The protein expression pattern of MaBAM9b remained consistently high throughout banana fruit ripening and starch degradation. Transient overexpression or inhibition of MaBAM9b in banana fruit greatly improved or suppressed starch degradation. Genetic modification of rice indicated that overexpression of MaBAM9b greatly improved starch degradation and seed germination, while inhibition of its expression suppressed these biological processes. These results support the key role of MaBAM9b in starch degradation and provide a target gene for banana fruit quality improvement and biological breeding.

内容编辑:
 地址:海南省海口市城西学院路4号(571101)
地址:海南省海口市城西学院路4号(571101) 电话:0898-66986419 传真:0898-66986419
电话:0898-66986419 传真:0898-66986419  E-mail:china_banana2008@vip.163.com
E-mail:china_banana2008@vip.163.com